Simple yet Detailed Introduction to Biochemistry
Do you have difficulty learning biochemistry? You must have difficulty learning about bioelements and biomolecules. Do you know what is metabolism and its types? If your answer is no then you are at the right place.
I have experience of a couple of years. I will teach you biochemistry from its definition and you will be surprised that this was so easy. Why didn’t I find this article before? Biochemistry was never so easy to understand. So, fasten your seatbelt to do a thorough read of this informative article. Let’s get started.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Biochemistry
Definition
The branch of biology which deals with the study of chemical components and chemical processes is called biochemistry.
According to the definition, biochemistry is divided into two parts; chemical components and chemical processes. Now, we will discuss these two parts, one by one in detail.
Chemical Components
Components mean small parts of a large whole. So, chemical components mean the elements or molecules which join to form large and complex compounds. We have two types of chemical components which are as follows:
- Bioelements
- Biomolecules
Bioelements
The elements of which living organisms are made up are called bioelements. There are 92 naturally occurring elements out of which 25 are bioelements. Out of the 25 bioelements, the human body is made up of only 16 elements.
Bioelements in the human body
As you know the human body is composed of 16 bioelements. These 16 elements are classified into three types based on their proportions in the human body which are as follows:
- Major bioelements
- Minor bioelements
- Trace Bioelements
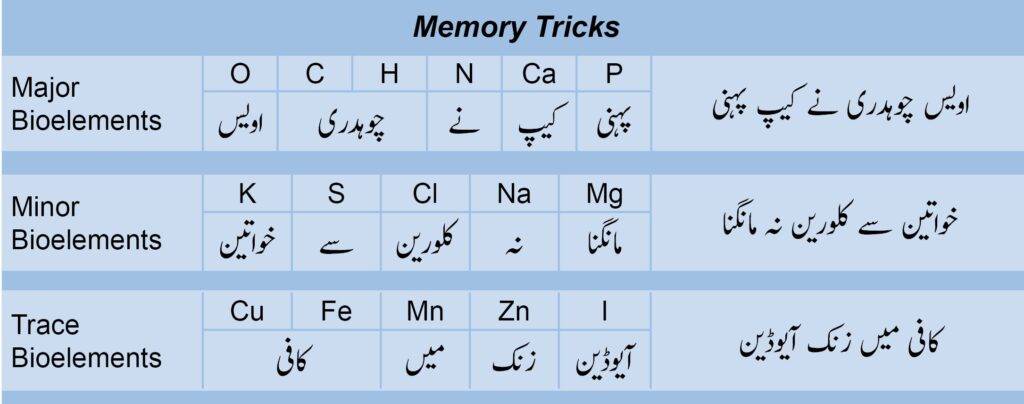
Major Bioelements
As the name suggests, major means they are present in the majority about 99% of the human body. Out of 16 bioelements in humans, 6 are major elements. These consist of the following elements
- Oxygen (O) – 65%
- Carbon (C) – 18%
- Hydrogen (H) – 10%
- Nitrogen (N) – 3%
- Calcium (Ca) – 2%
- Phosphorus (P) – 1%
These percentages sum up to 99%. You can remember these by a simple Urdu/Hindi sentence. Repeat this sentence 10 times in a row and you will remember it.
“Owais(O) Choudhry(C,H) Nay(N) Cap(Ca) Pehni(P) “
Minor Bioelements
Again, minor means they are present in the minority in human bodies which is less than 1%. Out of 16 bioelements in humans, 5 are minor elements. These elements are as follows:
- Potassium (K) – 0.35%
- Sulphur (S) – 0.25%
- Chlorine (Cl) – 0.15%
- Sodium (Na) – 0.15%
- Magnesium (Mg) – 0.05%
These values sum up to 0.95% which is less than 1%. You can remember them by a simple Urdu/Hindi sentence. Remember the drill, repeat it loudly 10 times in a row.
“Khawateen(K) Sy(S) Chlorine(Cl) Naa(Na) Mangna(Mg)“
Trace Bioelements
Trace elements are present in very very very low proportions in human bodies which is less than 0.01%. Out of 16 bioelements. 5 are trace elements which are as follows:
- Copper (Cu)
- Iron (Fe)
- Manganese (Mn)
- Zinc (Zn)
- Iodine (I)
You can remember them by a simple and easy Urdu/Hindi sentence. Remember the drill!
“Coffee(Cu,Fe) Main(Mn) Zinc(Zn) Iodine(I)”
The summary of these is shown in the image below
Biomolecules
When bioelements combine to form thousands of different and complex molecules, these molecules are called biomolecules. This was easy, right?
Types of Biomolecules
As bioelements had types so does biomolecules. There are two types of biomolecules:
- Organic Biomolecules
- Inorganic Biomolecules
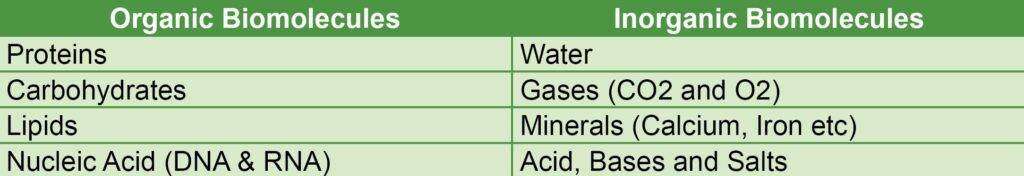
Organic Biomolecules
The molecules which contain carbon and hydrogen (C-H) covalent bonds are called organic biomolecules. There are only four biomolecules that are considered organic so, it wouldn’t be difficult to learn. Just to learn, say these are the Fantastic Four of biochemistry. They are listed as follows:
- Proteins
- Carbohydrates
- Lipids
- Nucleic Acids (DNA & RNA)
Inorganic Biomolecules
The molecules which do not contain C-H bonds are called inorganic biomolecules. Except, for four fundamental organic molecules all other molecules are under inorganic biomolecules. Some of the inorganic biomolecules are as follows:
- Water
- Gases like CO2 and O2
- Minerals like Ca++
- Acids, Bases and Salts
Also, read this – Memorize proportions of biomolecules in bacterial and mammalian cells
Chemical Processes
A method of changing one or more chemical components into other chemical components is called a chemical process. But, in living organisms, these chemical processes have a different name i.e. metabolism.
Metabolism & its types
All the chemical processes and reactions taking place in the human body are collectively called metabolism. There are two types of metabolism:
- Anabolism
- Catabolism
Anabolism
The process in which simpler substances join to form complex compounds is called anabolism.
It is a constructive process. Think, you are making a building. You are using smaller materials such as bricks, stones, sand etc to create a larger object i.e. a building. Just like that, the construction of complex molecules from simpler substances is anabolism.
The best example of anabolism is photosynthesis. As it ends with -synthesis so it means it includes synthesis. Remember, the process that involves synthesis is anabolism. In photosynthesis, light is used as a source of energy to synthesize glucose and oxygen from water and carbon dioxide. The energy from the sun is stored in the glucose molecule as ATP. So, remember anabolic reactions require energy.
Characteristics of Anabolism
The characteristics that we have learned from the above discussion are given below:
- Anabolism is involved in the synthesis of complex molecules
- Energy is required so the reaction to take place.
- Photosynthesis is an example of anabolism
Catabolism
This process is the reverse of anabolism. The process in which complex molecules are broken down into simpler substances is called catabolism.
If you find it difficult to remember whether catabolism or anabolism means to break or to synthesize, then I have a simple trick for you. The Urdu word “kaata” means to cut/to break. The word catabolism starts with cata- so assume it means to cut/to break. Hence, catabolism means a reaction in which complex molecules break. You should not forget this 😉
It is a destructive process. It’s just like destroying a large building into smaller pieces. So, a process that involves the destruction/breakdown of molecules is catabolism.
The best example of catabolism is respiration. In respiration, the glucose molecule is broken down into its components. As the glucose molecule breaks, the energy that was stored in it is released which is used in the human body for other complex processes. Hence, in catabolic reactions, the energy is released.
Characteristics of Catabolism
The characteristics of catabolic reactions that we learned from the discussion above are as follows:
- Catabolism is involved in the breakdown of complex substances/molecules
- Energy is released during a catabolic reaction.
- Respiration is an example of catabolism.
The complete difference between catabolism and anabolism is given in the table below

Quick Recap
A quick recap of all we have learned today is below
- Biochemistry has two parts chemical components and processes.
- Chemical components are bioelements are biomolecules.
- Bioelements have three types i.e. major (99% and are 6 out of 16), minor (less than 1% and are 5 out of 16) and trace elements (less than 0.01% and are 5 out of 16).
- Biomolecules are of two types i.e. organic (proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids) and inorganic (water, gases, minerals etc).
- Chemical processes taking place in living organisms are collectively called metabolism.
- Metabolism has two types i.e. anabolism (constructive, used energy, photosynthesis) and catabolism (destructive, release energy, respiration)
Conclusion
This was it! I have explained the basics of biochemistry merely from its definition. If you find it useful share it with your friends who are preparing for their entrance or intermediate examinations. Sharing knowledge always increases it. If you have any questions you can ask them in the comments or on the social media pages. Keep working hard and don’t give up on your dreams.
JOIN THE FACEBOOK GROUP
Join the community of MDCAT aspirants and keep learning new stuff from your fellow aspirants. When you are with like-minded people you always grow. You grow when you share your knowledge with others.
