Understanding Monomers and Polymers with a Brilliant Example
Do you have confusion between monomers and polymers? No problem, This complete article will help you remove the confusion and will refine your concept regarding monomers and polymers.
We will discuss what is a monomer, dimer and polymer. We will have a look at monomers that join to form the most essential biomolecules. When you finish this article, your questions will be answered and you will be confident about this topic. So, let’s get started.
Also, read this – Introduction to Biochemistry
Table of Contents
Introduction
In a chemical reaction, simple molecules combine to form large complex molecules and vice versa. The simple molecules are called monomers or macromolecules and the complex molecules are called polymers or macromolecules. At the end of this article, I have given a very good example which will make your concept crystal clear regarding monomers and polymers.
Monomers
Atoms or small molecules having a low molecular weight that joins to form large and complex molecules are called monomers. These are small subunits which may join together with similar subunits in a repeating fashion.
Etymology
The word “mono” means “one” and “meros” means “part. As a whole, monomers mean a single unit of a complex molecule/polymer.
Examples
The examples of monomers are as follows:
- Monosaccharides
- Amino acids
- Fatty acids
- Nucleotides
Dimers
When two monomers join the molecule formed as a result is called a dimer. The word “Di” means “two” and “meros” means “part”. So, dimer means a molecule which is made up of two monomers. An example of dimers is disaccharides.
Polymers
When a large number of monomers join to form large complex molecules they are called polymers. The monomers join by chemical bonds and they result in a polymer.
Etymology
The word “poly” means many and “meros” means “part”. So, polymer means a molecule which is made up of many single parts.
Examples
The examples of polymers are as follows:
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Lipids
- Nucleic acids
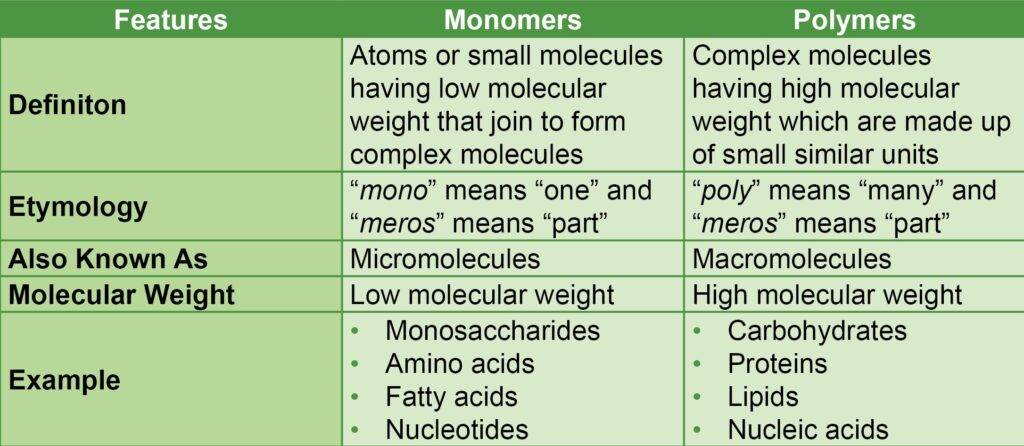
Differences between Monomers and Polymers
The differences between monomers and polymers are given in the table below:
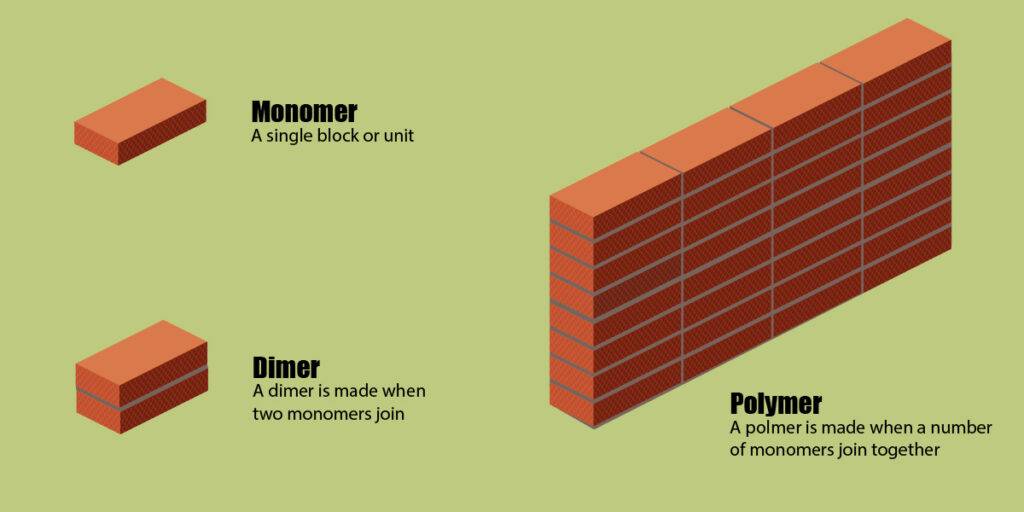
Monomers as Building Blocks
Like the bricks are the building blocks of buildings and cement is used to bond them together. Similarly, monomers are the building blocks of polymers and chemical bond holds these monomers together. Every polymer is not made up of the same monomers. Different monomers are used to make different polymers. A visual representation is given below:
Monomers of Essential Biomolecules
As you know there are four biomolecules which are essential for the proper functioning of living organisms. No living specie can live without them. The monomers of these polymers or biomolecules and the chemical bond which is used to hold them together are given below:
| Polymers | Monomers | Chemical Bond |
| Carbohydrates | Monosaccharides | Glycosidic Bond/Linkage |
| Proteins/Polypeptides | Amino Acids | Peptide Bond |
| Lipids | Fatty Acids and Glycerol | Ester Bond |
| Nucleic Acids | Nucleotides | Phosphodiester Bond |
Quick Recap
- Monomers are unit building blocks of polymers. Like, bricks are the building blocks of large buildings.
- When two monomers join the molecule formed is called a dimer.
- When a large number of monomers join they form a polymer.
Conclusion
So, that was the concept of monomers, dimers and polymers. I tried to explain it as simple as possible. Remember, monomers and polymers are part of the basic concepts of biochemistry. Make this concept strong so you can learn the difficult ones more easily. Share it with your friends and keep looking for more topics on the website. I will see you in the next article.
JOIN THE FACEBOOK GROUP
Join the community of MDCAT aspirants and keep learning new stuff from your fellow aspirants. When you are with like-minded people you always grow. You grow when you share your knowledge with others.
